Amazon Redshift Sink Connector for Confluent Cloud¶
The fully-managed Amazon Redshift Sink connector for Confluent Cloud allows you to export Avro, JSON Schema, or Protobuf data from Apache Kafka® topics to Amazon Redshift. The connector polls data from Kafka and writes this data to an Amazon Redshift database. Polling data is based on subscribed topics. Auto-creation of tables and limited auto-evolution are supported.
Note
- This Quick Start is for the fully-managed Confluent Cloud connector. If you are installing the connector locally for Confluent Platform, see Amazon Redshift Sink Connector for Confluent Platform.
- If you require private networking for fully-managed connectors, make sure to set up the proper networking beforehand. For more information, see Manage Networking for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
Features¶
- The Amazon Redshift Sink connector inserts Kafka records into an Amazon Redshift database.
- The connector supports Avro, JSON Schema, or Protobuf input data formats. Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
auto.createandauto-evolveare supported. If tables or columns are missing, they can be created automatically.- There is no primary key support.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Limitations¶
Be sure to review the following information.
- For connector limitations, see Amazon Redshift Sink Connector limitations.
- If you plan to use one or more Single Message Transforms (SMTs), see SMT Limitations.
- If you plan to use Confluent Cloud Schema Registry, see Schema Registry Enabled Environments.
Quick Start¶
Use this quick start to get up and running with the Confluent Cloud Amazon Redshift Sink connector. The quick start provides the basics of selecting the connector and configuring it to stream events to Amazon Redshift.
- Prerequisites
Authorized access to a Confluent Cloud cluster on Amazon Web Services.
The Confluent CLI installed and configured for the cluster. See Install the Confluent CLI.
Schema Registry must be enabled to use a Schema Registry-based format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
The Amazon Redshift database must be in the same region as your Confluent Cloud cluster.
For networking considerations, see Networking and DNS. To use a set of public egress IP addresses, see Public Egress IP Addresses for Confluent Cloud Connectors.
The connector configuration requires a Redshift user (and password) with Redshift database privileges. For example:
CREATE DATABASE <DB_NAME>; CREATE USER <DB_USER> PASSWORD '<DB_PASSWORD>'; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO <DB_USER>; GRANT CREATE ON SCHEMA public TO <DB_USER>; GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO <DB_USER>; GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public TO <DB_USER>; GRANT CREATE ON DATABASE <DB_NAME> TO <DB_USER>;
For additional information, see the Redshift docs.
- Kafka cluster credentials. The following lists the different ways you can provide credentials.
- Enter an existing service account resource ID.
- Create a Confluent Cloud service account for the connector. Make sure to review the ACL entries required in the service account documentation. Some connectors have specific ACL requirements.
- Create a Confluent Cloud API key and secret. To create a key and secret, you can use confluent api-key create or you can autogenerate the API key and secret directly in the Cloud Console when setting up the connector.
Using the Confluent Cloud Console¶
Step 1: Launch your Confluent Cloud cluster¶
See the Quick Start for Confluent Cloud for installation instructions.
Step 2: Add a connector¶
In the left navigation menu, click Connectors. If you already have connectors in your cluster, click + Add connector.
Step 4: Enter the connector details¶
Note
- Ensure you have all your prerequisites completed.
- An asterisk ( * ) designates a required entry.
At the Add Amazon Redshift Sink Connector screen, complete the following:
If you’ve already populated your Kafka topics, select the topics you want to connect from the Topics list.
To create a new topic, click +Add new topic.
- Select the way you want to provide Kafka Cluster credentials. You can
choose one of the following options:
- My account: This setting allows your connector to globally access everything that you have access to. With a user account, the connector uses an API key and secret to access the Kafka cluster. This option is not recommended for production.
- Service account: This setting limits the access for your connector by using a service account. This option is recommended for production.
- Use an existing API key: This setting allows you to specify an API key and a secret pair. You can use an existing pair or create a new one. This method is not recommended for production environments.
Note
Freight clusters support only service accounts for Kafka authentication.
- Click Continue.
- Enter the connection details:
- AWS Redshift domain: The domain leader node for the cluster. The
Redshift domain entered must be in the form:
<cluster-name>.<cluster-id>.<region>.redshift.amazonaws.com. - AWS Redshift port: The port number for incoming connections to the leader.
- Connection user: The username to authenticate with the database.
- Connection password: The password to authenticate with the database.
- Database name: The name of the database on the cluster.
- AWS Redshift domain: The domain leader node for the cluster. The
Redshift domain entered must be in the form:
- Click Continue.
Note
Configuration properties that are not shown in the Cloud Console use the default values. See Configuration Properties for all property values and definitions.
Select the Input Kafka record value format (data coming from the Kafka topic): AVRO, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or PROTOBUF. A valid schema must be available in Schema Registry to use a schema-based message format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf). See Schema Registry Enabled Environments for additional information.
Show advanced configurations
Schema context: Select a schema context to use for this connector, if using a schema-based data format. This property defaults to the Default context, which configures the connector to use the default schema set up for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment. A schema context allows you to use separate schemas (like schema sub-registries) tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry environment. For example, if you select a non-default context, a Source connector uses only that schema context to register a schema and a Sink connector uses only that schema context to read from. For more information about setting up a schema context, see What are schema contexts and when should you use them?.
Table name format: A format string for the destination table name, which may contain
${topic}as a placeholder for the originating topic name. For example, to create a table namedkafka-ordersbased on a Kafka topic namedorders, you would enterkafka-${topic}in this field.Database timezone: Name of the JDBC timezone that should be sed in the connector when inserting time-based values.
Batch size: Specifies how many records to attempt to batch together for insertion into the destination table.
Auto create table: Whether to automatically create the destination table if it is missing.
Auto add columns: Whether to automatically add columns in the table if they are missing.
For Transforms and Predicates, see the Single Message Transforms (SMT) documentation for details.
See Configuration Properties for all property values and definitions.
Click Continue.
Based on the number of topic partitions you select, you will be provided with a recommended number of tasks.
- To change the number of recommended tasks, enter the number of tasks for the connector to use in the Tasks field.
- Click Continue.
Step 5: Check the results in Redshift¶
- From the AWS Management Console, go to your Redshift project.
- Verify that new records are being added to the database.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Tip
When you launch a connector, a Dead Letter Queue topic is automatically created. See View Connector Dead Letter Queue Errors in Confluent Cloud for details.
Using the Confluent CLI¶
Complete the following steps to set up and run the connector using the Confluent CLI.
Note
Make sure you have all your prerequisites completed.
Step 1: List the available connectors¶
Enter the following command to list available connectors:
confluent connect plugin list
Step 2: List the connector configuration properties¶
Enter the following command to show the connector configuration properties:
confluent connect plugin describe <connector-plugin-name>
The command output shows the required and optional configuration properties.
Step 3: Create the connector configuration file¶
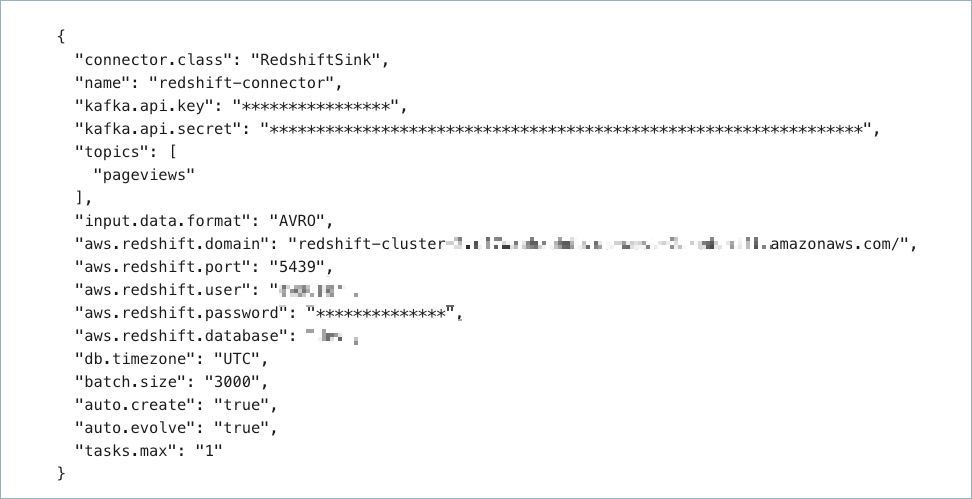
Create a JSON file that contains the connector configuration properties. The following example shows required and optional connector properties.
{
"name": "redshift-sink-connector",
"connector.class": "RedshiftSink",
"kafka.auth.mode": "KAFKA_API_KEY",
"kafka.api.key": "<my-kafka-api-key>",
"kafka.api.secret": "<my-kafka-api-secret>",
"topics": "<topic-name>",
"input.data.format": "AVRO",
"aws.redshift.domain": "<cluster-name>.<cluster-id>.<region>.redshift.amazonaws.com",
"aws.redshift.port": "5439",
"aws.redshift.user": "<redshift-username>",
"aws.redshift.password": "<redshift-user-password>",
"aws.redshift.database": "<redshift-database-name>",
"db.timezone": "UTC",
"auto.create": "true",
"auto.evolve": "true",
"tasks.max": "1"
}
Note the following property definitions:
"name": Sets a name for your new connector."connector.class": Identifies the connector plugin name.
"kafka.auth.mode": Identifies the connector authentication mode you want to use. There are two options:SERVICE_ACCOUNTorKAFKA_API_KEY(the default). To use an API key and secret, specify the configuration propertieskafka.api.keyandkafka.api.secret, as shown in the example configuration (above). To use a service account, specify the Resource ID in the propertykafka.service.account.id=<service-account-resource-ID>. To list the available service account resource IDs, use the following command:confluent iam service-account list
For example:
confluent iam service-account list Id | Resource ID | Name | Description +---------+-------------+-------------------+------------------- 123456 | sa-l1r23m | sa-1 | Service account 1 789101 | sa-l4d56p | sa-2 | Service account 2
"topics": Identifies the topic name or a comma-separated list of topic names."input.data.format": Sets the input Kafka record value format (data coming from the Kafka topic). Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR, or PROTOBUF. You must have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured if using a schema-based message format (for example, Avro, JSON_SR (JSON Schema), or Protobuf).aws.redshift.domain: This is the domain path to the cluster leader node. The Redshift domain entered must be in the form:<cluster-name>.<cluster-id>.<region>.redshift.amazonaws.com."db.timezone": (Optional) The timezone for the database. Defaults toUTC. For a list of valid entries, see tz database time zones."auto.create"(tables) and"auto-evolve"(columns): (Optional) Sets whether to automatically create tables or columns if they are missing relative to the input record schema. If not entered in the configuration, both default to"false"."tasks.max": Maximum number of tasks the connector can run. See Confluent Cloud connector limitations for additional task information.
Single Message Transforms: See the Single Message Transforms (SMT) documentation for details about adding SMTs using the CLI.
See Configuration Properties for all property values and definitions.
Step 4: Load the configuration file and create the connector¶
Enter the following command to load the configuration and start the connector:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file <file-name>.json
For example:
confluent connect cluster create --config-file redshift-sink-config.json
Example output:
Created connector redshift-sink-connector lcc-ix4dl
Step 5: Check the connector status¶
Enter the following command to check the connector status:
confluent connect cluster list
Example output:
ID | Name | Status | Type
+-----------+-------------------------+---------+------+
lcc-ix4dl | redshift-sink-connector | RUNNING | sink
Step 6: Check the results in Redshift.¶
- From the AWS Management Console, go to your Redshift project.
- Verify that new records are being added to the database.
For more information and examples to use with the Confluent Cloud API for Connect, see the Confluent Cloud API for Connect Usage Examples section.
Tip
When you launch a connector, a Dead Letter Queue topic is automatically created. See View Connector Dead Letter Queue Errors in Confluent Cloud for details.
Configuration Properties¶
Use the following configuration properties with the fully-managed connector. For self-managed connector property definitions and other details, see the connector docs in Self-managed connectors for Confluent Platform.
How should we connect to your data?¶
nameSets a name for your connector.
- Type: string
- Valid Values: A string at most 64 characters long
- Importance: high
Schema Config¶
schema.context.nameAdd a schema context name. A schema context represents an independent scope in Schema Registry. It is a separate sub-schema tied to topics in different Kafka clusters that share the same Schema Registry instance. If not used, the connector uses the default schema configured for Schema Registry in your Confluent Cloud environment.
- Type: string
- Default: default
- Importance: medium
Input messages¶
input.data.formatSets the input Kafka record value format. Valid entries are AVRO, JSON_SR and PROTOBUF. Note that you need to have Confluent Cloud Schema Registry configured
- Type: string
- Importance: high
Kafka Cluster credentials¶
kafka.auth.modeKafka Authentication mode. It can be one of KAFKA_API_KEY or SERVICE_ACCOUNT. It defaults to KAFKA_API_KEY mode.
- Type: string
- Default: KAFKA_API_KEY
- Valid Values: KAFKA_API_KEY, SERVICE_ACCOUNT
- Importance: high
kafka.api.keyKafka API Key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
- Type: password
- Importance: high
kafka.service.account.idThe Service Account that will be used to generate the API keys to communicate with Kafka Cluster.
- Type: string
- Importance: high
kafka.api.secretSecret associated with Kafka API key. Required when kafka.auth.mode==KAFKA_API_KEY.
- Type: password
- Importance: high
Which topics do you want to get data from?¶
topicsIdentifies the topic name or a comma-separated list of topic names.
- Type: list
- Importance: high
How should we connect to your Redshift?¶
aws.redshift.domainThe domain leader node for the cluster. The domain entered must be in the form: <cluster-name>.<cluster-id>.<region>.redshift.amazonaws.com
- Type: string
- Importance: high
aws.redshift.portPort number for incoming connections to the leader.
- Type: int
- Default: 5439
- Valid Values: [0,…,65535]
- Importance: high
aws.redshift.userUsername to authenticate with the database.
- Type: string
- Importance: high
aws.redshift.passwordPassword to authenticate with the database.
- Type: password
- Importance: high
aws.redshift.databaseName of the database on the cluster.
- Type: string
- Importance: high
Database details¶
table.name.formatA format string for the destination table name, which may contain ‘${topic}’ as a placeholder for the originating topic name.
For example, kafka_${topic} for the topic ‘orders’ will map to the table name ‘kafka_orders’.
- Type: string
- Default: ${topic}
- Importance: medium
db.timezoneName of the JDBC timezone that should be used in the connector when inserting time-based values. Defaults to UTC.
- Type: string
- Default: UTC
- Importance: medium
Connection details¶
batch.sizeSpecifies how many records to attempt to batch together for insertion into the destination table.
- Type: int
- Default: 3000
- Valid Values: [1,…,5000]
- Importance: medium
SQL/DDL Support¶
auto.createWhether to automatically create the destination table if it is missing.
- Type: boolean
- Default: false
- Importance: medium
auto.evolveWhether to automatically add columns in the table if they are missing.
- Type: boolean
- Default: false
- Importance: medium
Consumer configuration¶
max.poll.interval.msThe maximum delay between subsequent consume requests to Kafka. This configuration property may be used to improve the performance of the connector, if the connector cannot send records to the sink system. Defaults to 300000 milliseconds (5 minutes).
- Type: long
- Default: 300000 (5 minutes)
- Valid Values: [60000,…,1800000] for non-dedicated clusters and [60000,…] for dedicated clusters
- Importance: low
max.poll.recordsThe maximum number of records to consume from Kafka in a single request. This configuration property may be used to improve the performance of the connector, if the connector cannot send records to the sink system. Defaults to 500 records.
- Type: long
- Default: 500
- Valid Values: [1,…,500] for non-dedicated clusters and [1,…] for dedicated clusters
- Importance: low
Number of tasks for this connector¶
tasks.maxMaximum number of tasks for the connector.
- Type: int
- Valid Values: [1,…]
- Importance: high
Next Steps¶
For an example that shows fully-managed Confluent Cloud connectors in action with Confluent Cloud ksqlDB, see the Cloud ETL Demo. This example also shows how to use Confluent CLI to manage your resources in Confluent Cloud.
Try Confluent Cloud on AWS Marketplace with $1000 of free usage for 30 days, and pay as you go. No credit card is required.